中文, Español, Português
US-China commerce tensions have negatively affected shoppers in addition to many producers in each international locations. The tariffs have decreased commerce between the US and China, however the bilateral commerce deficit stays broadly unchanged. Whereas the affect on world progress is comparatively modest at the moment, the most recent escalation may considerably dent enterprise and monetary market sentiment, disrupt world provide chains, and jeopardize the projected restoration in world progress in 2019.
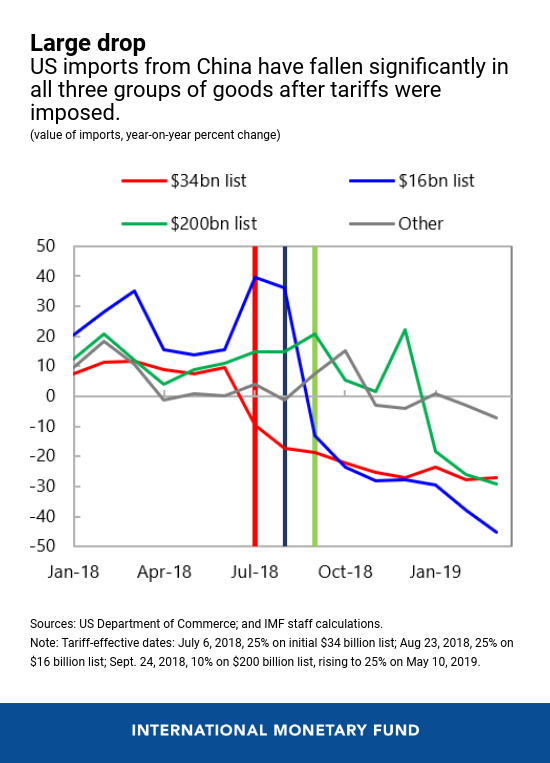
Evolution of commerce within the US and China
The elevating of US tariffs to 25 % on $200 billion of annual Chinese language imports on Could 10, along with the introduced Chinese language retaliation, marks the most recent escalation within the US–China commerce tensions.
The affect of beforehand imposed tariffs by the US and subsequent retaliation by China is already evident in commerce knowledge. Each the international locations instantly concerned and their buying and selling companions have been affected by rising tariffs.
In 2018, the US imposed tariffs sequentially on three “lists” of products from China, concentrating on first $34 billion of annual imports, then $16 billion extra, and at last an extra $200 billion. In consequence, US imports from China have declined fairly sharply in all three teams of the products on which tariffs have been imposed.
In instances the place there was a delay between announcement and implementation of tariffs, as within the case of the $16 billion and $200 billion lists, or plans to section within the tariff improve, as within the case of the $200 billion checklist, we noticed a rise in import progress prematurely of the efficient dates. This means that importers stocked up forward of the tariffs, accounting for the sharper decline in imports thereafter.
As China imposed retaliatory tariffs, US exports to China additionally declined. Whereas the front-loading dynamic just isn’t evident on this case, US export progress to China has been usually weaker for the reason that commerce tensions started.
Results on shoppers
Shoppers within the US and China are unequivocally the losers from commerce tensions. Analysis by Cavallo, Gopinath, Neiman and Tang, utilizing value knowledge from the Bureau of Labor Statistics on imports from China, finds that tariff income collected has been borne nearly solely by US importers. There was nearly no change within the (ex-tariff) border costs of imports from China, and a pointy soar within the post-tariff import costs matching the magnitude of the tariff.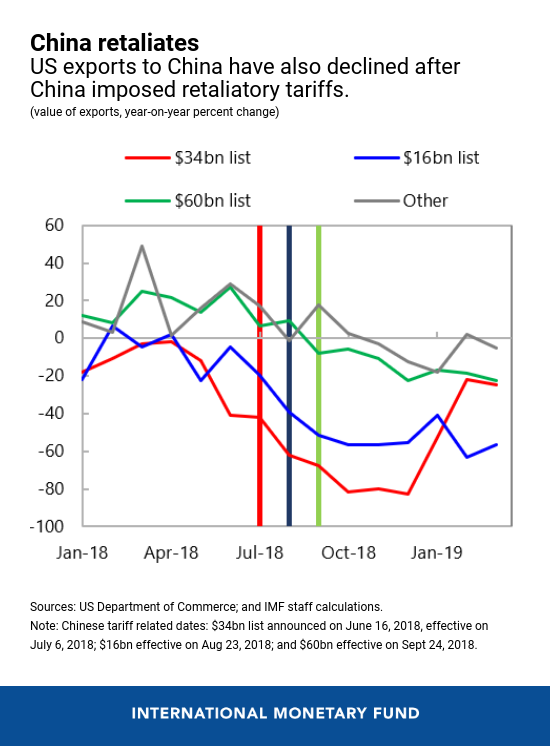
A few of these tariffs have been handed on to US shoppers, like these on washing machines, whereas others have been absorbed by importing corporations via decrease revenue margins. An extra improve in tariffs will doubtless be equally handed via to shoppers. Whereas the direct impact on inflation could also be small, it may result in broader results via a rise within the costs of home rivals.

Results on producers
The impact on producers is extra blended, with some winners and lots of losers. Some US and Chinese language producers of products competing in home markets with imports affected by tariffs, in addition to competing third nation exporters, are potential winners. 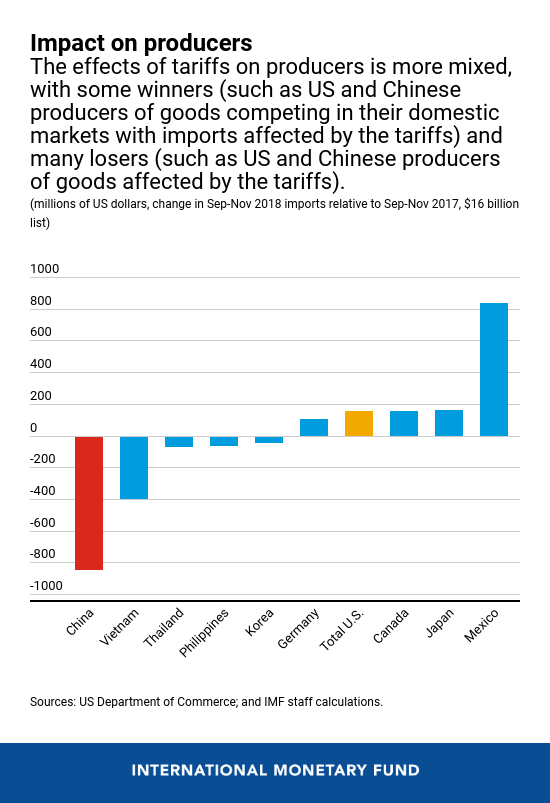 Nonetheless, US and Chinese language producers of the products affected by the tariffs in addition to producers that use these items as intermediate inputs, are potential losers.
Nonetheless, US and Chinese language producers of the products affected by the tariffs in addition to producers that use these items as intermediate inputs, are potential losers.
Commerce diversion is one channel via which producers are affected. Aggregated bilateral US knowledge does counsel that commerce diversion has occurred, because the decline in imports from China seems to have been offset by a rise in imports from different international locations.
For instance, US imports from Mexico elevated considerably amongst some items on which the US imposed tariffs. After the $16 billion checklist was applied in August, a pointy decline of almost $850 million in imports from China was nearly offset by about $850 million improve from Mexico, leaving general US imports broadly unchanged. For different international locations corresponding to Japan, Korea and Canada, one can observe smaller will increase in US imports relative to the degrees in September-November 2017. After all, mixture knowledge could possibly be masking different components driving the bilateral commerce patterns, corresponding to using inventories. For instance, there was little or no change in imports from third international locations within the case of photosensitive semiconductor units.
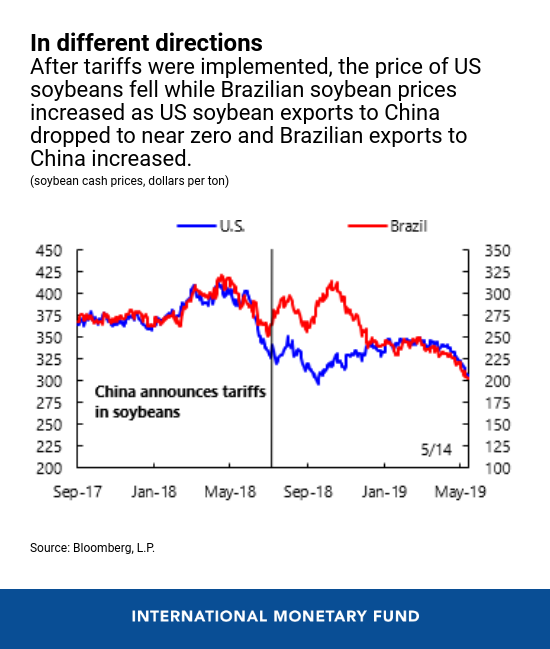
The opposite channel by which producers could possibly be affected is thru market segmentation within the value of traded items. This was most clearly noticed within the case of soybeans, the place US exports to China fell dramatically in 2018 after China imposed tariffs. The USA was China’s dominant soybean provider, together with Brazil, in 2017. With the tariffs, the value of US soybeans fell whereas that of Brazilian soybeans elevated, as US exports to China dropped to close zero and Brazilian exports to China trended greater. Although costs have since re-converged and soybean exports to China have resumed to some extent, US soybean farmers suffered, whereas these in Brazil benefited from commerce diversion and market segmentation.
The affect on US producers with vital publicity to Chinese language markets was additionally captured in inventory market valuations. As an illustration, the fairness value efficiency of US firms with excessive gross sales to China underperformed relative to US companies uncovered to different worldwide markets, after tariffs linked to the $34 billion retaliation checklist by China have been applied.
The hole narrowed firstly of 2019 with the commerce truce. However it reopened once more after the US tariff improve to 25 % on the $200 billion checklist was introduced on Twitter.

Macroeconomic results
The ratcheting up of bilateral tariffs between the US and China has had restricted impact on their bilateral commerce steadiness. Actually, in 2018, the commerce deficit elevated for the US as imports from China rose, which partly displays the front-loading. As of March 2019, a small decline will be noticed, however US exports to China are additionally falling.
Certainly, macroeconomic components—together with relative mixture demand and provide in accomplice international locations and their underlying drivers—play a a lot greater function than tariffs in figuring out bilateral commerce balances.

On the world stage, the extra affect of the not too long ago introduced and envisaged new US-China tariffs, anticipated to increase to all commerce between these international locations, will subtract about 0.3 % of worldwide GDP within the quick time period, with half stemming from enterprise and market confidence results. The IMF’s forthcoming G-20 Surveillance Observe in early June will present additional particulars. These results, whereas comparatively modest at the moment, come on high of tariffs already applied in 2018.
Furthermore, failure to resolve commerce variations and additional escalation in different areas, such because the auto business, which might cowl a number of international locations, may additional dent enterprise and monetary market sentiment, negatively affect rising market bond spreads and currencies, and gradual funding and commerce.
As well as, greater commerce obstacles would disrupt world provide chains and gradual the unfold of recent applied sciences, finally reducing world productiveness and welfare. Extra import restrictions would additionally make tradable client items much less reasonably priced, harming low-income households disproportionately. Such a situation is among the many explanation why we referred to 2019 as a fragile 12 months for the worldwide financial system.
Associated Hyperlinks:
April 2019 World Financial Outlook
October 2018 World Financial Outlook

